Chevron Indonesia has started production from the Bangka Field in the Kutei Basin offshore East Kalimantan following an investment decision by the company in 2014 and subsequent Indonesian government approvals. Development drilling commenced in September 2014.

Geology
The 60,000 km2 Kutei basin extends from the central highlands of Borneo, across the eastern coast of the island and into the Makassar Strait. It is the largest Tertiary basin in Indonesia with up to 15 km of sediment. The Kutei is an extensional basin in a foreland tectonic setting. Extension began in the Mid Eocene with subsequent thermal sag, and isostatic subsidence. Rapid, high volume, sedimentation related to uplift and inversion began in the Early Miocene.
Syn-rift deposition in the Eocene was focused in small, localised depocenters within individual half-grabens. The initial graben fill is highly variable due to the wide zone of rifting, and ranges from fully terrestrial in the western basin, to entirely marine in the eastern basin. Syn-rift sedimentation following the initial graben fill is variable across the basin, but several distinct facies tracts have been identified. Non marine, deltaic, shallow marine, deep marine and carbonate platform syn-rift deposits are found in the basin.
Sag phase deposition began in the Upper Eocene to Oligocene. A regional depocenter developed in response to marine transgression. The eastern basin, already influenced by marine conditions quickly transitioned to a deep marine depositional environment, while the western basin transitioned more slowly. A thick marine shale was deposited across much of the basin, while carbonate sedimentation continued on along the basin margin and across topographic highs.
Large carbonate platforms developed along the basin margins as the result of shallowing marine environments in the early phases of the Late Oligocene tectonic inversion combined with a marine regression. As tectonic uplift of central Borneo continued into the lower Miocene, the westernmost portion of the Kutai Basin was inverted above sea level, forming the Upper Kutai Basin.\n\nIn the Early Miocene large amounts of clastic sediment derived from the rising central mountains, and the now inverted Paleogene flowed into the lower Kutai Basin. Basin inversion in the middle Miocene and Pliocene saw a shift in the deltaic depo-centre eastwards into the Makassar Straight.
Neogene sediments in the vicinity of the modern Mahakam delta are up to 9 kilometres thick with total sediment thickness of up to 15 km.
Production & Development
In the Kutei Basin in East Kalimantan, most of the Chevron production has come from 14 offshore fields in the shelf area within the East Kalimantan PSC, with the remainder from the deepwater West Seno Field in the Makassar Strait PSC.\n\nThe development will be the first deep-water subsea tieback thus far in Indonesia and will utilise subsea well connections to the West Seno FPU. It will also be Indonesia’s first deepwater flexible pipeline and the first single deepwater umbilical installed.
Nameplate production capacity in this initial development stage is 110 MMcf/d of natural gas and 4,000 b/d of condensate. Chevron has a 62% operating interest in the Bangka project with ENI SA holding a 20% interest and Tip Top Energy Ltd with 18% interest.
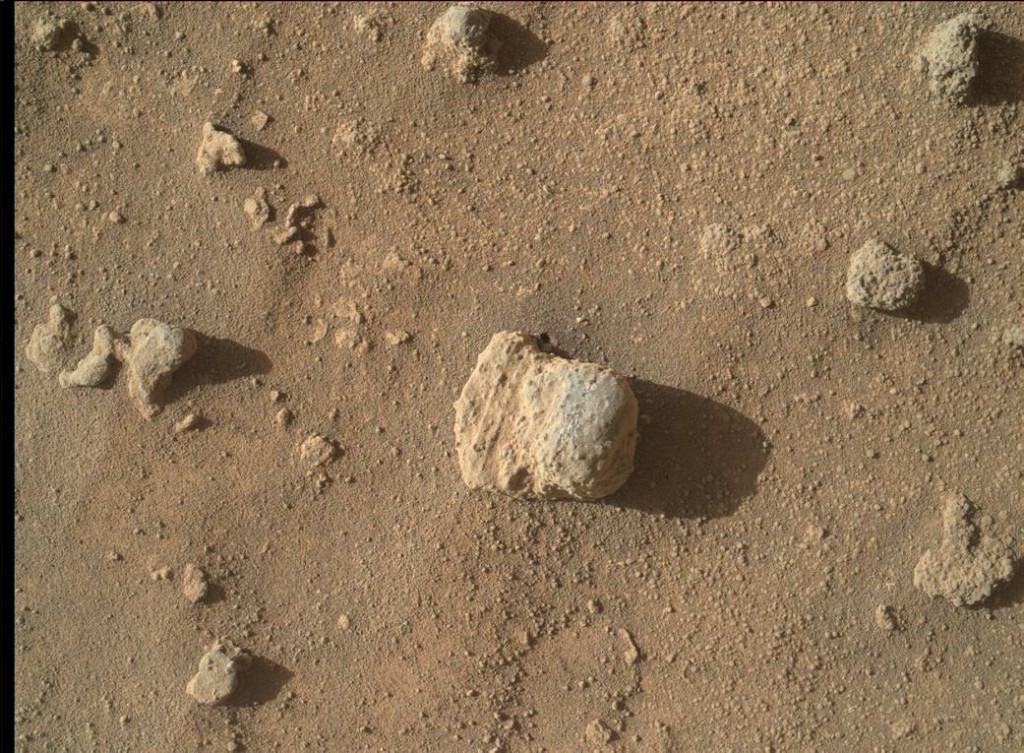

 This rock was photographed a couple of days ago using the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover. Curiosity has now been operational on Mars for 1, 282 days.
This rock was photographed a couple of days ago using the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover. Curiosity has now been operational on Mars for 1, 282 days.